This series of articles dives deeper into the actual applications of Machine Learning that are currently in use in many current technological processes and devices.

Through these posts entitled “Machine Learning is Fun!”, Adam Geitgey guides us step by step through the concepts, data, algorithms, code, results and pitfalls of machine learning applications from image, face and speech recognition to language translation and more. It also gathers several different sources for more details on each application and its development.
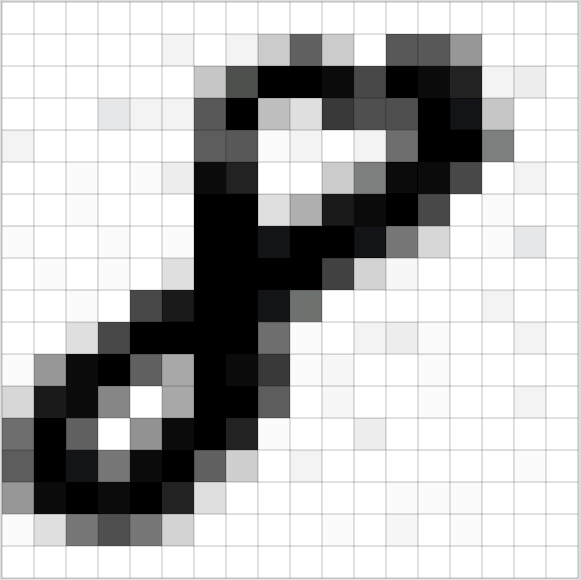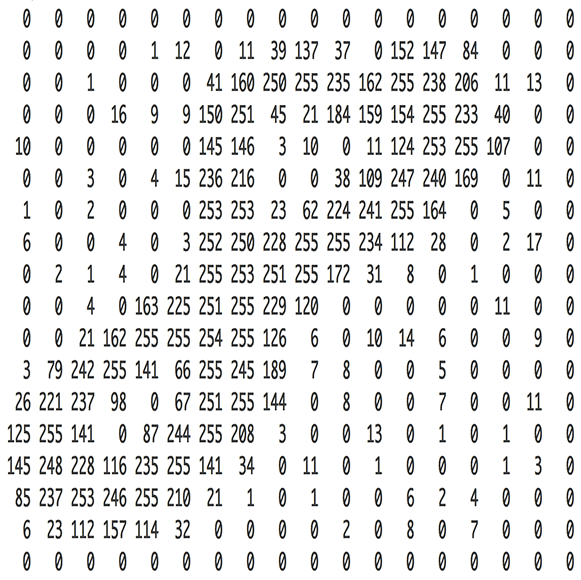
This series is really dense with detailed code, but it is also explained very clearly, step by step, with detailed illustration. It notably covers the use of a Convolutional Neural Network (including Generative Adversarial Network) and Recurrent Neural Network, together with some of their most prominent applications in daily life. It is a real course not to be missed for any ML developer!
Here is the list of posts with direct links:
- Part 1: The world’s easiest introduction to Machine Learning
- Part 2: Using Machine Learning to generate Super Mario Maker levels
- Part 3: Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks
- Part 4: Modern Face Recognition with Deep Learning
- Part 5: Language Translation with Deep Learning and the Magic of Sequences
- Part 6: How to do Speech Recognition with Deep Learning
- Part 7: Abusing Generative Adversarial Networks to Make 8-bit Pixel Art
- Part 8: How to Intentionally Trick Neural Networks