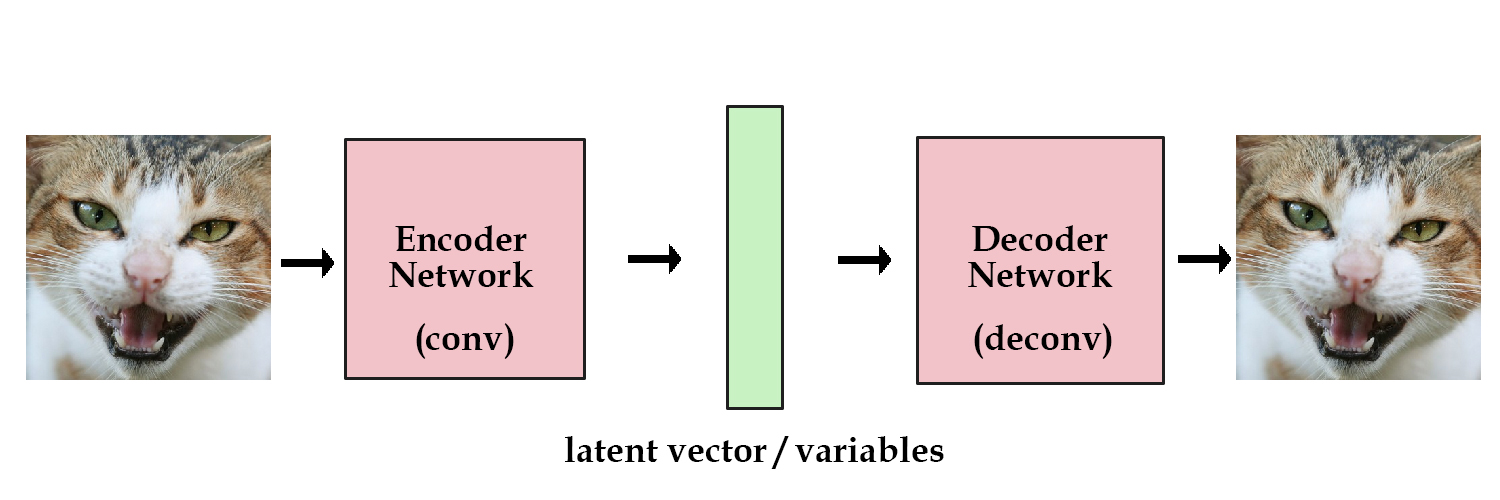
A Variational Autoencoder – VAE – is a type of neural network used to generate data of various types, and especially images. VAEs use an encoder (a convolutional network) and a decoder (a deconvolutional network) in order to extract a latent vector from sample data. This latent vector can then be used with arbitrary parameters to generate new data.
For more information, read this presentation of VAEs and this complete tutorial on VAEs.
« Back to Glossary Index